Consumption-Based Pricing
Table of Contents
What is Consumption-Based Pricing?
Consumption-based pricing is a pricing model that charges customers based on their product or service usage. Consumption-based pricing calculates pricing based on usage volume rather than the number of users and is a popular pricing model for IT services, SaaS, and cloud computing and storage. Since customers only pay for the resources they use, this pricing model can result in significant savings.
Under a consumption-based pricing model, customers are typically charged for the resources they use on a per-unit basis. For example, a customer who uses more electricity or bandwidth than another customer would be charged a higher price. This type of pricing can be advantageous for customers with low levels of consumption, as they would pay lower prices than under a traditional fixed-price model.
While many providers offer different consumption-based plans, some require a commitment to a minimum term and/or maximum capacity. In addition, some providers limit the number of devices that can access the same account simultaneously.
Read on to learn more about this complex pricing model, its advantages, and challenges.
Synonyms
- pay-as-you-go pricing (PAYG)
- flexible consumption pricing
- usage-based pricing
- SaaS consumption model
- consumption as a service
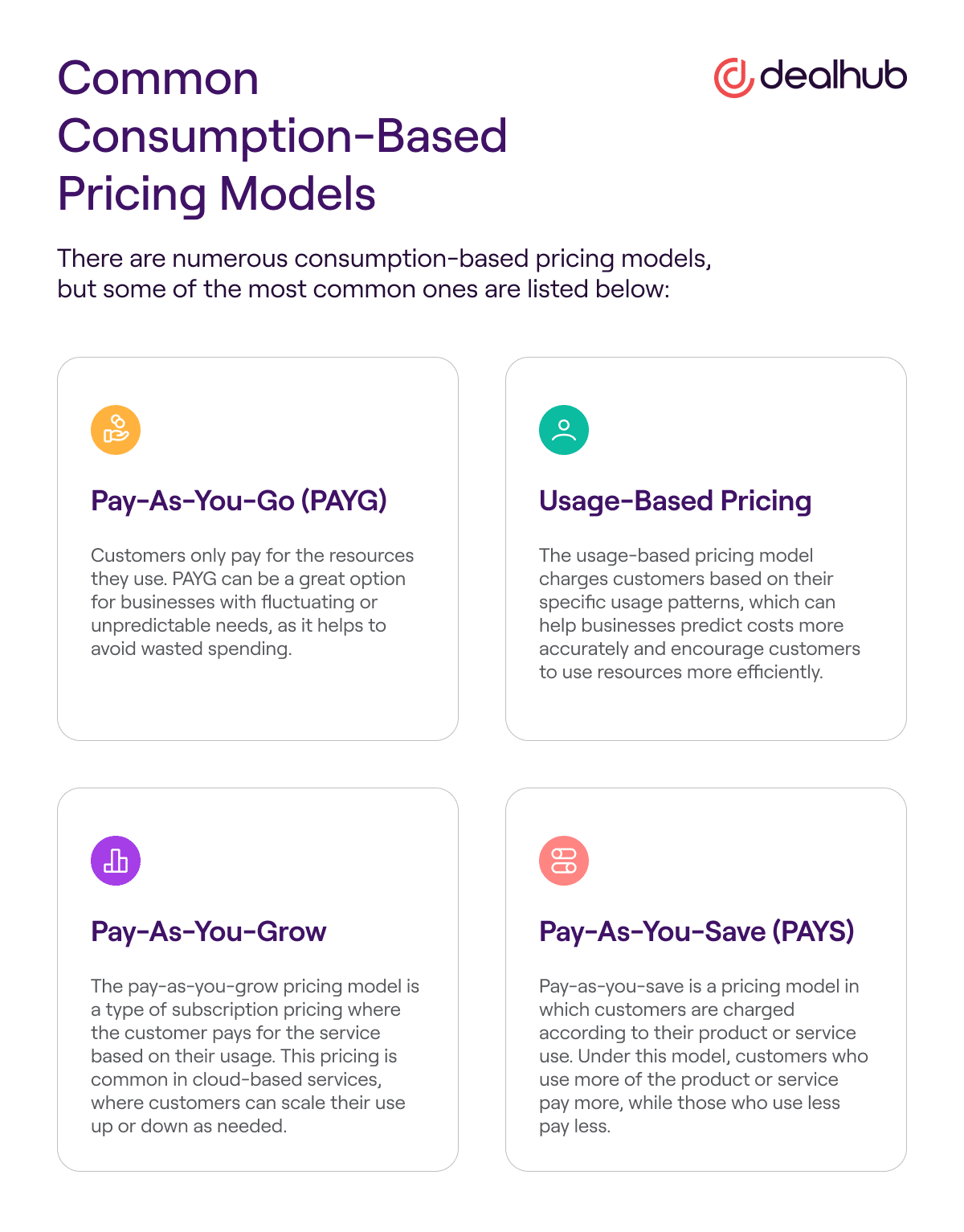
Common Consumption-Based Pricing Models
There are numerous consumption-based pricing models, but some of the most common ones are listed below:
Pay-As-You-Go (PAYG)
With pay-as-you-go pricing, customers only pay for the resources they use. PAYG can be a great option for businesses with fluctuating or unpredictable needs, as it helps to avoid wasted spending. However, it can also be challenging to estimate costs in advance, and businesses may need to be prepared for spikes in usage (and associated costs).
Usage-Based Pricing
The usage-based pricing model charges customers based on their specific usage patterns, which can help businesses predict costs more accurately and encourage customers to use resources more efficiently. However, it can be difficult to establish the right pricing structure, and usage-based models can be complex to administer.
Pay-As-You-Grow
The pay-as-you-grow pricing model is a type of subscription pricing where the customer pays for the service based on their usage. This pricing is common in cloud-based services, where customers can scale their use up or down as needed. Pay-as-you-grow pricing can be a flexible and cost-effective way to pay for services since customers only pay for what they use.
Pay-As-You-Save (PAYS)
Pay-as-you-save is a pricing model in which customers are charged according to their product or service use. Under this model, customers who use more of the product or service pay more, while those who use less pay less.
The PAYS model is becoming increasingly popular in the energy industry as it encourages conservation and can help reduce the demand on resources.
With the PAYS model, businesses can also offer discounts to customers who use less of their product or service, which can further incentivize conservation and help to lower prices for everyone.
Benefits of a Consumption-Based Pricing Model
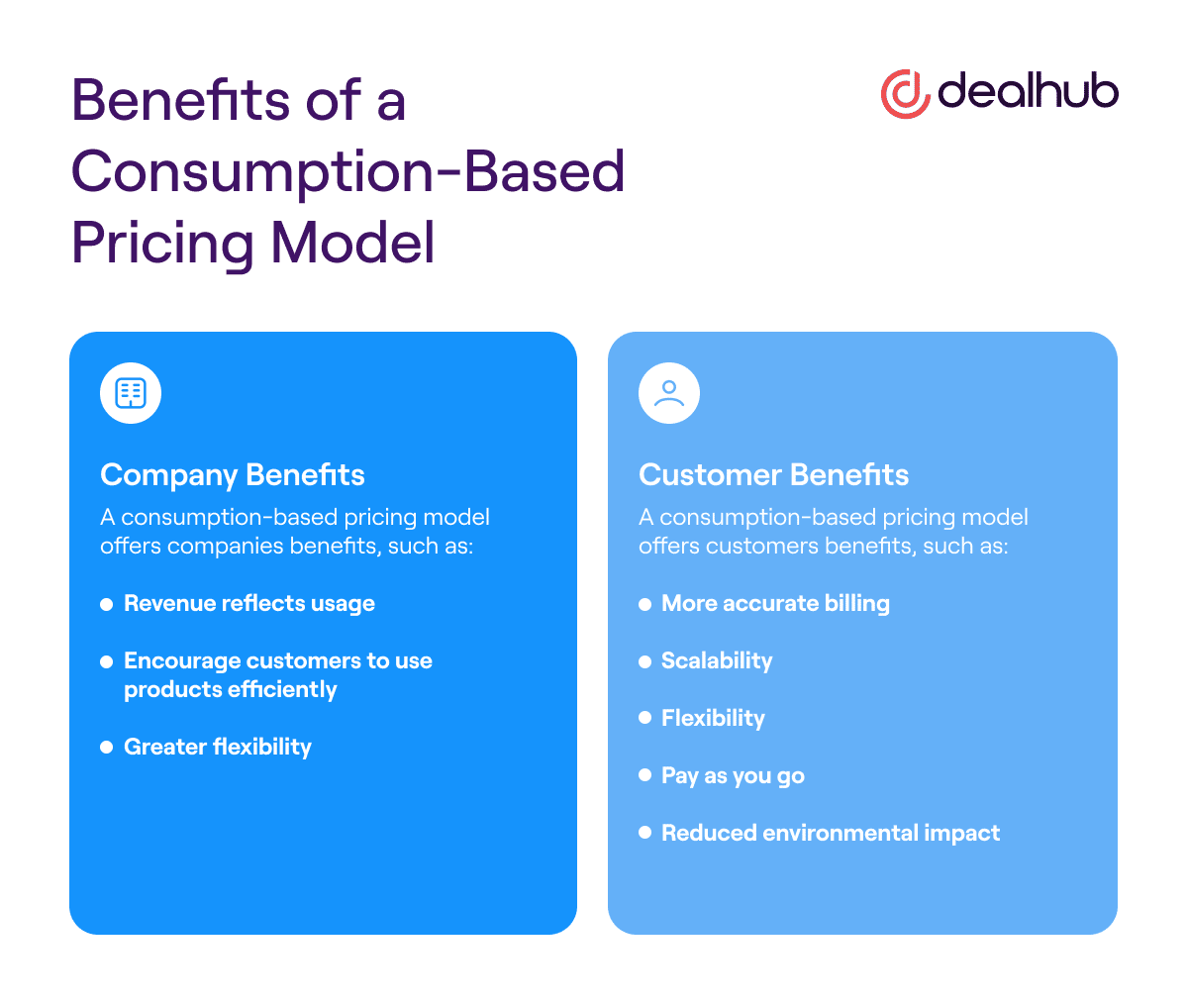
Company Benefits
A consumption-based pricing model has several benefits for companies, including:
- Revenue reflects usage: Perhaps most importantly, this pricing model can help to match recurring revenue more closely with actual usage. This can be helpful in budgeting and forecasting. It also gives the vendor a better understanding of which products or services are used most frequently.
- Encourage customers to use products efficiently: By aligning cost with usage, customers will likely be more conscious of how they use your product or service and may be less likely to waste resources.
- Greater flexibility: Consumption-based pricing models can offer greater flexibility, benefiting companies with unpredictable or fluctuating usage patterns. Consumption-based pricing can also be more responsive to changes in customer demand, making it easier to respond to market trends.
Customer Benefits
A consumption-based pricing model offers customers benefits, such as:
- More accurate billing: With a consumption-based model, businesses only pay for the resources they use, which can help customers avoid overspending on resources that are not needed.
- Scalability: A consumption-based model can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing business needs.
- Flexibility: It offers customers more flexibility in resource use.
- Pay as you go: With a consumption-based model, businesses can pay for resources as they are used rather than upfront. This can help to save money on resources that may not be used regularly.
- Reduced environmental impact: By only using the necessary resources, businesses can help reduce their environmental impact.
Challenges in Implementing Consumption-Based Pricing
Implementing a consumption-based pricing strategy can be challenging for businesses. When selling products as a service, companies must find the right balance between providing customers with value and generating enough revenue to cover their costs. This can be difficult, as pricing too high will discourage customers from purchasing, while pricing too low will result in a loss for the company.
Another challenge is that accurately predicting consumption patterns can be complex, particularly in volatile markets or where customer behavior changes rapidly. This can lead to pricing errors and unexpected costs for businesses.
Consumption-based pricing can also be complex to administer and manage, requiring close monitoring of customer usage patterns. This can be resource intensive and may require specialized expertise.
In addition, customers charged based on consumption pay their bill after consuming the service, which can present a cash flow problem for some companies.
Finally, some customers may resist or object to paying prices that fluctuate based on usage, preferring more predictable pricing structures. Implementing consumption-based pricing, therefore, requires careful planning and consideration of all potential risks and challenges.
Despite these challenges, consumption-based pricing can offer many benefits, including improved customer satisfaction and loyalty and increased efficiency and profitability.
When done well, consumption-based business models be a powerful tool to increase sales, improve customer retention, and drive operational efficiencies. However, there are many challenges that companies must overcome to implement them successfully.
People Also Ask
What is the advantage of using a consumption-based model?
There are several advantages of using a consumption-based model to price services.
First, it allows businesses to only pay for the resources they consume, which can save money compared to other pricing models where customers pay a fixed rate regardless of how much they use.
Second, consumption-based pricing is more flexible and can be adapted as business needs change. For example, if a business needs to increase its service usage, it can do so without
renegotiating its contract or worrying about exceeding a set limit.
Third, consumption-based models often include discounts for volume customers, making them more affordable for businesses that use large amounts of resources.
Finally, many providers offer “pay as you go” options with no long-term commitment, so businesses can start and stop using a service as needed without penalty.
Overall, consumption-based pricing provides various advantages for businesses, including lower costs, more flexibility, and the ability to pay only for what is used. It also helps SaaS vendors align with their customers’ needs and grow with them over time.
What is a flexible consumption model?
A consumption-based business model is also known as a flexible consumption model (FCM), a pricing model that allows customers to pay for goods or services according to their usage. This means that customers only pay for what they use when they use it. Flexible consumption models can be used for various products and services, from cloud computing to pay-as-you-go cell phone plans.
Flexible consumption models offer some advantages for both businesses and consumers. For businesses, flexible consumption models can help to reduce costs and increase efficiency. For consumers, flexible consumption models can provide greater choice and control over how they spend their money.
What is consumption as a service?
Consumption as a service is a model of business in which customers can access and use a product or service on an as-needed basis, typically through a subscription. For example, software and cloud-based services often use this business model, where customers can pay for only the service they use rather than making a lump-sum payment upfront.
The consumption-as-a-service model has several advantages for both businesses and customers. For businesses, it can provide a more predictable revenue stream and help to manage costs better. For customers, it can offer greater flexibility and convenience, as well as the ability to scale usage up or down as needed.
One potential downside of the consumption-as-a-service model is that it can sometimes be less cost-effective in the long run than other models, such as purchasing a product outright. However, for many businesses and consumers, the flexibility and convenience of consumption as a service outweigh the potential drawbacks.