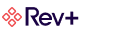Complex Pricing Models
Table of Contents
What is a Complex Pricing Model?
A complex pricing model is a pricing strategy that considers multiple factors to determine the price of a product or service. These models are often used in industries where many variables affect the price of the goods or services offered.
Complex pricing models often consider factors such as the cost of production, the demand for the product or service, the competition in the market, and any discounts or promotions that may be available. By considering all of these factors, businesses can come up with a price that will allow them to make a profit while still being competitive in the market.
Complex pricing models are more sophisticated than traditional ones and often involve multiple variables. As a result, they can be more challenging to understand and predict. However, complex pricing models can also offer greater flexibility and potential for profitability.
There are a variety of complex pricing models in use today, and the most appropriate model for a given business will depend on factors such as the products or services being offered, the competitive landscape, and the company’s overall strategy. Common pricing models include variable pricing, tiered pricing, subscription pricing, and usage-based pricing. These are defined in more detail below.
Synonyms
- complex pricing strategy
- usage-based pricing
- subscription pricing model
- tiered pricing model
- bundled pricing
Simple vs. Complex Pricing
There are two main types of pricing models: simple and complex. Simple pricing models are typically used for products or services that are relatively straightforward, such as a single item with a fixed price. On the other hand, complex pricing models are used for products or services that are more complicated and can involve multiple factors such as time, volume, or usage.
One of the main differences between simple and complex pricing models is the possible level of customization. Simple pricing models are usually less customizable because the price is based on a single factor that is not likely to change. Complex pricing models, however, are more flexible and customizable because they consider multiple factors.
Another difference between simple and complex pricing models is the level of risk. Simple pricing models usually have less risk because the price is based on a single factor. On the other hand, complex pricing models can have more risk because the factors can fluctuate.
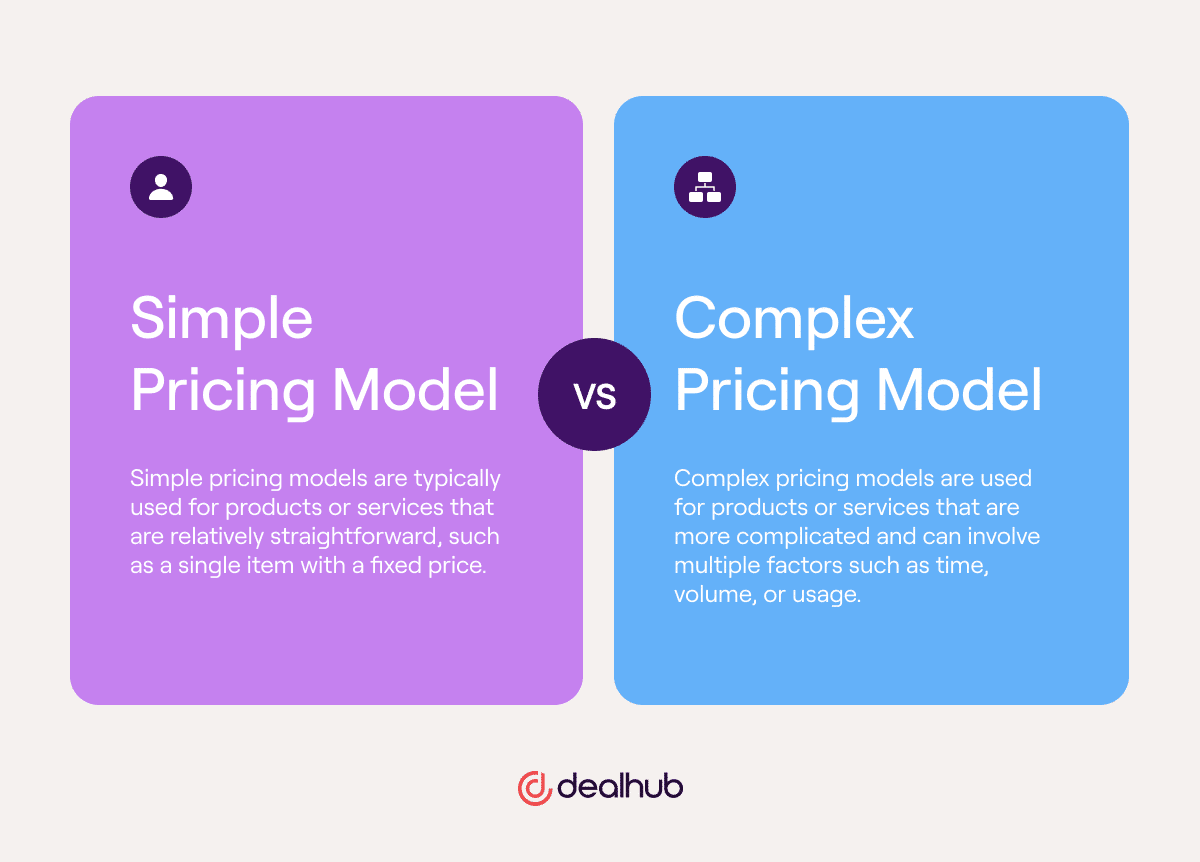
The Four Cs of Pricing Your Product
Correctly pricing your product is one of the most crucial steps in your go-to-market strategy. The wrong price can lead to lost sales and revenue, so it’s critical to get it right. The best way to do this is to follow the Four Cs of Pricing Your Product.
Cost: Your price must cover the cost of manufacturing, developing, or acquiring the product, as well as any other associated costs like shipping and handling.
Competition: Be aware of what other businesses are charging for similar products, and make sure that your price is competitive.
Customer value: Your price should reflect the value your customer will get from the product.
Channel: Your price should be appropriate for the sales channel through which it will be sold.
Types of Complex Pricing Strategies
Bundled Pricing
Bundling products together into a package is a way for companies to offer their products at a lower price than they would if they sold each product separately. Bundling is ubiquitous across multiple industries, where it is used to increase sales by offering a lower price for customers who purchase multiple products.
Variable Pricing
Variable pricing is a model in which prices vary based on factors such as time of day, day of the week, or location. This pricing strategy can encourage customers to purchase during off-peak times and can be used to account for differences in demand or cost between different locations.
Tiered Pricing
Tiered pricing is a pricing strategy in which companies charge different prices for their products or services based on quality or features. For example, a company may charge a higher fee for its premium product and a lower price for its basic product. Pricing tiers can differentiate products and encourage potential customers to purchase the more expensive, higher-quality product. Tiered pricing is standard in enterprise software, where customers pay for access to specific modules within a larger package.
Digital Product Pricing
Digital product pricing is the process of setting a price for a digital product. There are many digital pricing models, but the most common are subscription-based and pay-per-use.
Subscription-based pricing is when a customer pays a set price for access to a product or service for a set time. This could be monthly, yearly, or even longer. Pay-per-use pricing is when a customer pays for each use of the product or service. This could be per project, per month, or even per hour.
The pricing model you use will depend on the type of product or service you are offering and your business goals. For example, if you are selling a digital product that is used infrequently, pay-per-use pricing may be a better option. On the other hand, if you are selling a digital product that is used frequently, subscription-based pricing may be a better option.
Subscription Pricing
Subscription pricing is a pricing model where customers pay a recurring fee to access a product or service. This pricing model is common in subscription-based businesses such as those in the software as a service (SaaS) industry, where customers typically pay a monthly or annual fee to use a software application. Subscription pricing can also be used for physical products, such as when customers pay a monthly fee to receive a subscription box of products.
Examples of subscription pricing models are:
- Usage-Based Model – Usage-based pricing is a model in which customers are charged based on their level of use of a product or service. This type of pricing is common for utilities like electricity or water and can help to align costs with consumption.
- Per-Added-Module Model – The Per-Added-Module Model is a billing model used by some software companies. Under this model, the customer pays a fee for each additional module they add to the software. This can be an attractive option for customers who only need a few extra features and don’t want to pay for an entirely new software package.
- Per-User Model – Per-user pricing model is a type of pricing in which the price of a product or service is based on the number of users using it. This type of pricing is common among SaaS products. Under this pricing model, companies typically charge a certain amount for each user that signs up for their service. This pricing model is beneficial for companies because it allows them to scale their prices according to the number of users they have. It is also beneficial for customers because they only have to pay for a set number of users.
Services Pricing
There are many different ways to price services. The most common is the hourly rate model, where the client is charged based on the number of hours worked by the service provider. Other popular models include project-based pricing, where the client is charged a set fee for the entire project, and value-based pricing, where the client is charged based on the perceived value of the service.
Volume Pricing
Volume pricing is a pricing strategy where businesses offer discounts to customers who purchase large quantities of goods or services. This pricing type can encourage customers to buy more products, which can help companies to increase their sales and profits. Volume pricing can also help businesses clear out inventory, as customers may be more likely to purchase discounted products.
There are a few different ways that businesses can offer volume pricing discounts. One way is to offer a tiered discount, where customers receive a greater discount the more product they purchase. Another way is to offer a bulk discount, where customers receive a set percentage off their purchase if they buy a specific product quantity. Businesses can also offer a mix-and-match discount, where customers receive a discount if they purchase a certain combination of products.
Economy Pricing
In an economy pricing model, businesses charge a price based on what they believe the customer is willing and able to pay. This can be determined by analyzing the customer’s income, spending habits, and other factors. Businesses often use an economy pricing model to maximize profits, but it can also encourage customers to purchase more products or services.
Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing is a dynamic pricing strategy where a company offers a low price for its product or service to gain market share. The hope is that once the company has gained a significant market share, it will be able to raise prices. Penetration pricing is common in technology because new products are introduced frequently.
Penetration pricing is risky, as it can often lead to price wars with competitors. If a company cannot gain market share quickly, it may find itself in a position where it is losing money on each sale. Nevertheless, penetration pricing can be an effective way to enter a new market.
Price Skimming
Price skimming is another dynamic pricing strategy in which a company charges a high price for a new product during its initial release and then gradually lowers the price as demand decreases. Price skimming can effectively maximize profits and recoup investments quickly, but it can also lead to intense competition from lower-priced products.
Price skimming is often used for products that are new to the market and have few substitutes. For example, when a new video game console is released, there may be a time during which only a few companies sell the console at a high price. As more companies enter the market and competition increases, the console price will gradually decrease.
Premium Pricing
Premium pricing is a strategy where a company charges a higher price for a product or service than what is considered to be the norm. The goal of premium pricing is to create the perception of value and quality and to increase profits.
There are several ways to implement premium pricing. For example, companies can charge more for a product that is seen as being of higher quality, or they can offer premium features or services for an additional fee (i.e. tiered pricing). Premium pricing can also be used to target a specific market segment, such as luxury consumers.
When done correctly, premium pricing can be a successful way to increase profits and build brand equity. However, it is essential to consider all aspects of the strategy before implementing it, as risks can be involved. For example, if a company overcharges for a product, it can lower customer satisfaction with the brand. Thus, it is essential to conduct market research and understand consumer behavior before implementing a premium pricing strategy.
Many complex pricing models are in use today, and new models are constantly being developed. The key for businesses is to select the model (or combination of models) that best meets their needs and objectives.
How to Use CPQ to Produce Quotes from Complex Pricing Models
If you’re working with complex pricing models such as subscription pricing or tiered pricing, you will find that using a CPQ (configure, price, quote) tool can be extremely helpful in generating quotes. Here’s a quick overview of how to use CPQ to produce quotes from complex pricing models:
First, you’ll need to create a pricing model template within your CPQ software. This template will serve as the foundation for your quotes and should include all relevant pricing information for your products or services.
Once you have your pricing model template set up, you can begin creating individual quotes. You’ll simply need to input the required information (such as customer contact information, product quantities, etc.), and the CPQ software will generate a quote based on your pricing model.
If you need to make any changes to your quotes, you can do so easily within the CPQ software. Make the necessary adjustments and the software will update the quote accordingly.
If you’re wondering if it’s the right time to consider a CPQ, using CPQ to generate quotes from complex pricing models can save you considerable time and effort. In addition, with CPQ, you can be sure that your quotes are accurate and up-to-date, making the quoting process much simpler and more efficient.
People Also Ask
What are pricing models used for?
Pricing strategies or models determine the best product or service prices. It helps you decide which products to sell at which price points to maximize revenue and shareholder value while considering customer and market demand.
How is a price model determined?
A price model considers factors such as the costs involved in making an item, the customer’s perception of its value, and the type of product — for example, retail goods versus services.
They are usually visually represented on a chart like a demand curve.
What are the three pricing factors?
You need to consider three key pricing factors when setting the price for your product or service.
These are:
1. The cost of production or delivery
2. The demand for your product or service
3. The competition in your market