Request for Proposal (RFP)
Table of Contents
What Is Request for Proposal?
A request for proposal, or RFP, is a document that solicits proposals from vendors to select the best company to provide a product or service. The RFP generally includes an overview of the organization’s needs, as well as information about the vendor’s qualifications and proposal submission requirements.
In some cases, the RFP may also include a timeline for project completion and/or a list of desired features. Vendors respond to the RFP with their proposals, which the organization then evaluates to select the best option.
The RFP process can be used for various products and services, from office supplies to software development.
Synonyms
- Call for Proposal
A call for proposal, or CFP, is a request for vendors to submit proposals for a project.
What Is the Importance of RFPs In Business?
By using a request for proposal, organizations can be sure that they are getting the best products and services for the best value. And by allowing multiple companies to compete for their business, organizations can encourage vendors to be innovative in their proposals.
RFPs can also help organizations to save time and money by streamlining the vendor selection process. By clearly outlining their needs and requirements in an RFP, organizations can avoid spending valuable time and resources evaluating proposals that do not meet their needs.
RFPs help to build sales relationships with vendors. When vendors and organizations have a clear and open line of communication from the start of the RFP process, it can set the tone for a productive and positive relationship going forward.
The Process of Compiling an RFP
Creating a proposal request is not a simple task. The RFP must be well-written and thoroughly researched to ensure that all of the organization’s needs are met.
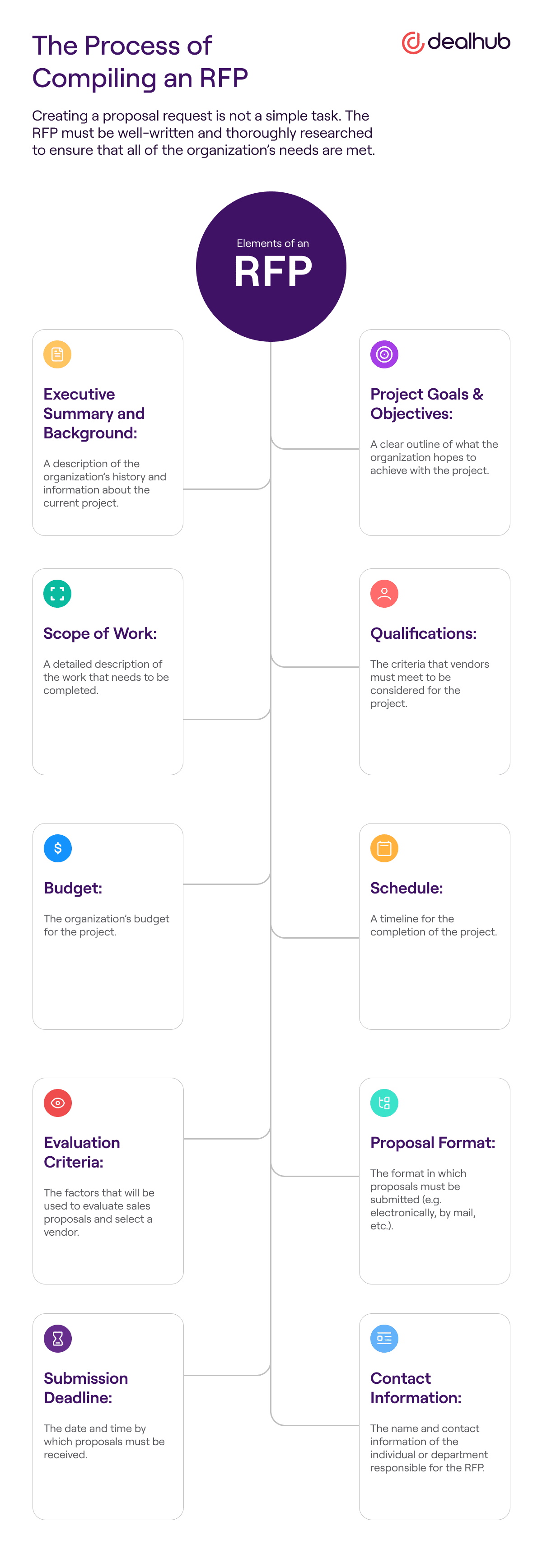
Elements of an RFP
Each RFP will have different elements, depending on the product or service being procured. However, some common elements are typically included in most RFPs, such as:
- Executive Summary and Background: A description of the organization’s history and information about the current project.
- Project Goals and Objectives: A clear outline of what the organization hopes to achieve with the project.
- Scope of Work: A detailed description of the work that needs to be completed.
- Qualifications: The criteria that vendors must meet to be considered for the project.
- Budget: The organization’s budget for the project.
- Schedule: A timeline for the completion of the project.
- Evaluation Criteria: The factors that will be used to evaluate sales proposals and select a vendor.
- Proposal Format: The format in which proposals must be submitted (e.g. electronically, by mail, etc.).
- Submission Deadline: The date and time by which proposals must be received.
- Contact Information: The name and contact information of the individual or department responsible for the RFP.
According to LinkedIn, organizations respond to 65% of their RFPs. By including all of these elements in the RFP, businesses can ensure that they will receive comprehensive proposals from as many qualified leads as possible.
Process
Writing a sales proposal begins with defining the organization’s needs. It is helpful to consult with stakeholders and subject matter experts to identify the business challenge.
Once the business challenge has been identified, the organization can begin Creating a business case.
This first document in the request for proposal process will detail:
- The problem the business has identified
- Its impact on productivity, finances, and the organization’s overall bottom line
- The ROI of procurement (as an estimation)
Once leadership and all other stakeholders have signed off on the business case, the organization can begin to develop specifications for what they need from a vendor.
These requirements should be clear, concise, and specific. Once the organization has compiled a list of their requirements, they can begin developing the request for proposal document.
First, the business will have to write a request for proposal executive summary and background information.
The RFP executive summary is the business’s opportunity to “sell” the project to potential vendors. It should include information about the organization’s history and the current problem they hope to solve with procurement.
In the executive summary, businesses should include:
- An overview of the organization’s history
- Information about the current project
- The organization’s goals and objectives for the project
The vendor may not be familiar with the organization’s history, so being descriptive is essential when writing a proposal request.
Once the organization completes the executive summary, it can move on to the scope of work.
The scope of work should be a detailed description of all the work that needs to be completed.
This section should include:
- A comprehensive list of deliverables, including any milestones that the vendor must meet
- A timeline for the project
- Any milestones that the vendor needs to meet
- The project budget
After the scope of work, businesses should include a section on qualifications.
This section will list the criteria that vendors must meet to be considered for the project. This may include:
- Experience working on similar projects
- Specific skills or expertise
- Experience, certifications, or licenses that the vendor must have
- The ability to meet the timeline
- The ability to work within the project budget
It is also helpful to order the selection criteria by order of importance so that the vendor understands which criteria are essential and can craft a proposal that best highlights their abilities.
Once all of this information is laid out, the RFP writer will need to explain how the vendors should respond. By writing the structure for the proposal, businesses can ensure that they receive proposals that are easy to compare.
Depending on the project’s complexity, the request for proposal may be several pages long or be comprised of bullets and headlines.
The final step in writing a request for proposal is to include all of the necessary information for responding. This will include:
- The name and contact information of the individual or department responsible for the RFP
- The submission deadline
- Any instructions on how to submit the proposal
By including all of these elements in the RFP, organizations can ensure that they will receive proposals that are clear, concise, and responsive to their needs.
Examples
When it comes to writing requests for proposals, there are many different types.
The three most common request for proposal examples are:
- Consulting request for proposal
- IT request for proposal
- Marketing request for proposal
A consulting request for proposal is used when an organization is looking to hire a consultant to help them with a specific project. This type of RFP will request information about the consultant’s experience, qualifications, and proposal for the project.
An IT request for proposal is used when an organization is looking to procure new software or hardware through a single developer, agency, or software company. This request for proposal will ask for information about the vendor’s product, pricing, and implementation plan.
A marketing request for proposal is used when an organization is looking to hire a marketing firm to help them with a specific campaign. This kind of RFP will request information about the firm’s niche experience, proposed marketing strategy, and estimated budget.
How to Respond to an RFP?
Before writing your response to a request for proposal, vendors should have a clear understanding of what the organization is looking for. This means reading the RFP carefully and ensuring they have all the information they need to write a responsive proposal. Vendors should reach out to the organization for clarification before responding if there are any questions about the RFP.
Once vendors clearly understand the RFP requirements, they can start writing their responses. The proposal should be clear, concise, and well-organized so that the review committee can easily understand what is being offered. And most importantly, vendors should prioritize personalization in their proposals.
Request for proposal responses should also match the format requested in the RFP. For example, if the RFP request that proposals be submitted as PDFs, vendors should ensure that their response is submitted in that format.
It is also noteworthy that many organizations will request that vendors not include additional materials with their proposals (such as brochures or marketing materials). In these cases, only the information that is specifically requested in the RFP should be submitted.
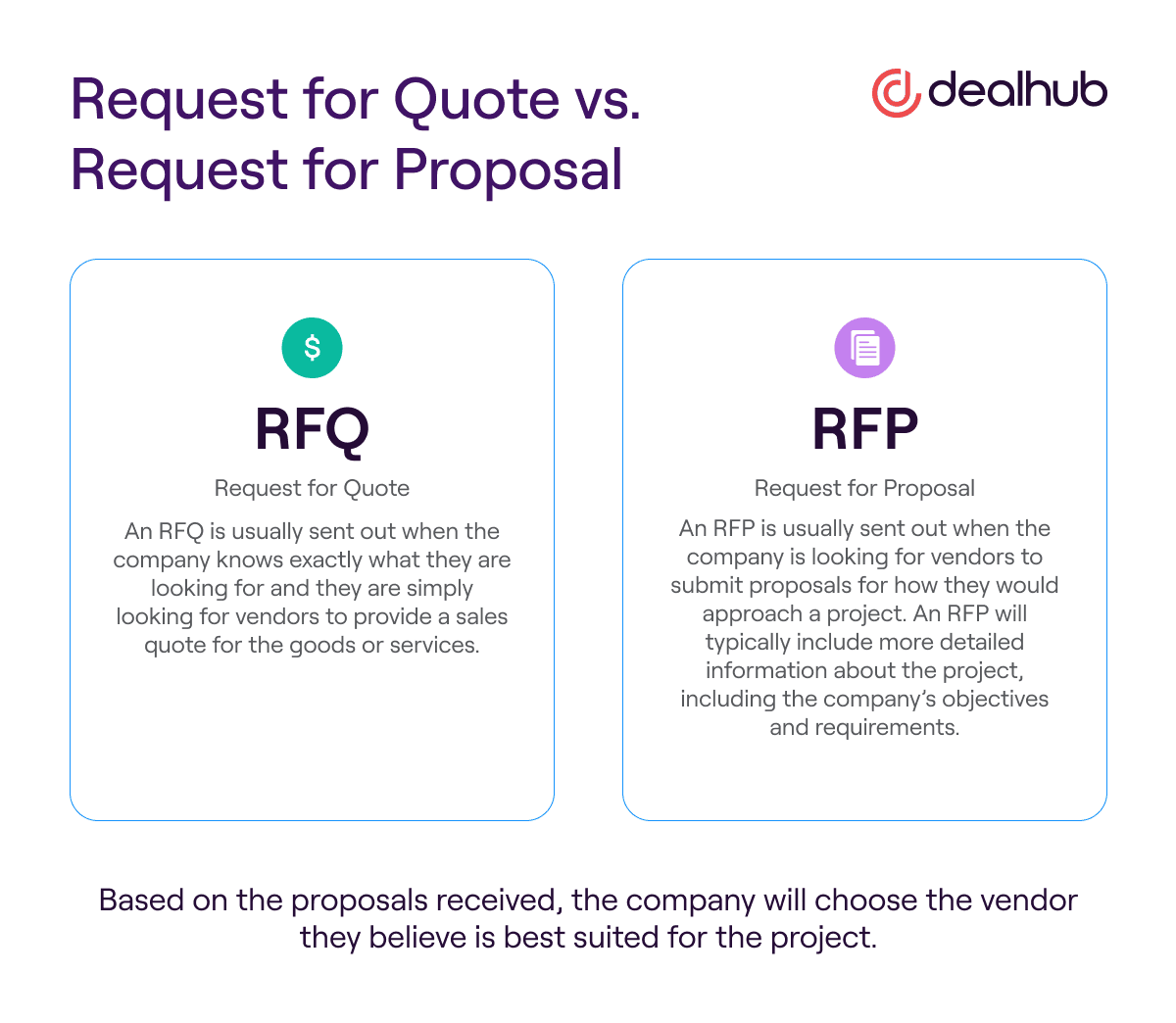
Request for Quote vs. Request for Proposal
When a company is looking to procure goods or services, they may send out a request for quote (RFQ) or a request for proposal (RFP). Both RFQs and RFPs are tools that allow companies to gather information from vendors to make an informed decision about which vendor to use.
So, what is the difference between a request for quote vs. a request for proposal?
An RFQ is usually sent out when the company knows exactly what they are looking for and they are simply looking for vendors to provide a sales quote for the goods or services.
In contrast, an RFP is usually sent out when the company is looking for vendors to submit proposals for how they would approach a project. An RFP will typically include more detailed information about the project, including the company’s objectives and requirements. Based on the proposals received, the company will choose the vendor they believe is best suited for the project.
Why Your RFP Responses are Failing
On average, organizations win 44% of their RFPs. If a vendor has been responding to request for proposals but hasn’t had any success, it’s important to take a step back and assess why your RFP responses are failing.
There several reasons why an RFP response may not be successful, including:
- The proposal is too long and/or difficult to understand.
- The vendor did not accurately demonstrate its value proposition.
- The proposal does not address the specific requirements of the RFP.
- The submission is not tailored to the company/organization.
- The vendor does not have enough experience.
When writing a request for proposal response, it’s important to keep these potential pitfalls in mind. Vendors can increase their chances of success by ensuring that your proposal is clear, concise, and tailored to the company.
When a business fails to get enough responses from vendors or the quality of responses is poor, it may be time to re-evaluate the request for proposal process.
A few common errors in writing proposal requests include:
- Asking for too much information
- Not being specific enough about what is needed
- Failing to provide enough context
- Making the process too long or cumbersome
If a company is having trouble getting quality request for proposals, they should take a look at their request for proposal process to see if any areas can be improved.
Benefits of Using an RFP Template for CPQ Software
Whether you’re looking for CPQ software for the first time or upgrading your existing system, using a request for proposal template is a great way to compare CPQ vendors.
Since CPQ software is a complex and technical solution, it’s important to clearly understand your company’s specific needs before starting the search for a new system. A request for proposal template can help with this by providing a structure for vendors to follow when responding to your RFP.
In addition, using an RFP template can help ensure that all of the important information is covered in each vendor’s proposal. This can make it easier to compare and contrast different systems side-by-side, ultimately leading to a better decision about which CPQ software is right for your business.
When writing a request for proposal for CPQ software, be sure to include:
- An overview of your company and your specific CPQ needs
- A list of desired features and functionality
- An overview of your budget
- A timeline for the project
By including all of this information in your RFP, you can be sure that each vendor is on the same page and can provide you with a proposal that meets all of your requirements.
People Also Ask
What does a request for proposal include?
A request for proposal, or RFP, is a document that businesses use to find the best possible vendors for their needs.
The RFP typically includes an overview of the company’s needs and a detailed description of the work the vendor would be expected to perform. In addition, the RFP may also include information on the company’s budget and timeline for the project.
Vendors use this information to prepare their proposals, which they submit to the company for review. The company then evaluates the proposals and selects the vendor that they feel is best suited for the job.
Who writes an RFP?
Sometimes, business owners or project stakeholders will write the RFP themselves. In other cases, the company may hire request for proposal services to create the document on their behalf.
In either case, the goal of the RFP is to attract qualified vendors and generate proposals that can be evaluated and compared to choose the best possible option for the company.
How do I submit an RFP?
When you’re ready to submit an RFP, the organization that prepared the RFP will include instructions on how to do so. Typically, you’ll need to fill out a form with your contact information and some details about your proposal.
Once you’ve submitted the form, your RFP will be reviewed by the organization’s team. If they’re interested in learning more about your proposal, they’ll contact you to set up a meeting or call.
From there, it’s up to you to give them the best possible pitch for why your proposal is the right fit for their needs. But remember: even if you don’t win the RFP, submitting one is a great way to get your foot in the door and start building relationships with potential clients.
What is RFP in contracts?
In a contract, an RFP is issued by one party to another party or parties, asking them to submit a proposal for the goods or services they are seeking.
The RFP will include information on what the buyer is looking for and any terms and conditions attached to the deal. Once the proposals have been received, the buyer will review them and select the one that best meets their needs.
RFPs are commonly used in government contracts, as well as in business-to-business deals. By issuing an RFP, buyers can ensure that they receive proposals from a wide range of providers, streamlining the contract management process.

